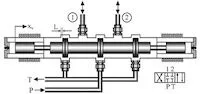
Valves Used for Chemical Systems
Apr 20, 2023
In various chemical industrial production, valves are indispensable important equipment components and devices. The valve is a device that cuts off, adjusts, changes the direction of the medium, controls the pressure of the medium, separates water and gas in the medium, and ensures the safety of the pipeline system in the pipeline. Therefore, the correct selection, operation and maintenance of the valve are very important. In addition, the valve is also a device that controls the medium in the pipeline. It is treated as a pressure-bearing component on the pipeline device, but it is a valve that varies with the operation method, medium used, temperature, pressure, pipeline structure, and use. To make good valves, the structure is very important, but the selection of materials is more important. It is even more important to understand the thermal processing method of materials and to choose the correct thermal processing method, but the importance of cold processing to the processing quality of valve parts and the influence of assembly on valve performance cannot be ignored.
1. Characteristics of the valve
As a pipeline device, the valve has three characteristics: use, structure, and driving.
Characteristics of use: The use performance and scope of use are determined when a valve is designed. The use characteristics of the valve include the category of the valve, the type of the valve, the main parts of the valve, and the driving mode of the valve.
Structural characteristics: It determines some structural characteristics of valve installation, maintenance and repair. Structural characteristics are the structural length and overall height of the valve, the connection form with the pipeline, the form of the sealing seat, and the processing form of the valve stem.
Driving characteristics: There are two working characteristics of the valve; one is driven by an external force, and the other is driven by the force or medium force generated by the deformation of the internal parts of the valve.
2. Inspection of the valve
After the valve arrives at the place of delivery, the purchaser shall unpack and inspect the valve according to the requirements of the order, and carefully check whether the quantity, size, pressure rating, connection, valve body and bonnet materials, appearance quality, accessories (spare parts), and protective measures of the valve meet the requirements. After the valve is accepted, it should be placed indoors. The large-diameter valve should be placed outdoors with protective measures for inspection and testing. For the valves sent directly to the construction site, after the inspection and test, they should be placed in a clean place and covered to prevent dust and other foreign objects from entering.
3. Testing the valve
Generally speaking, the valve should be tested for valve strength and sealing performance before installation. 20% of low-pressure valves should be spot-checked, and 100% of medium and high-pressure valves should be tested to ensure the safe use of the valve.
When liquid generally water is used as the test medium, the air in the valve should be removed as much as possible to prevent the pressure value from being unstable during the pressure test. During the pressure test, the pressure should be increased gradually and slowly, and it is not allowed to increase the pressure suddenly to prevent accidents. The selection of the pressure gauge should be within 25 to 75% of the range of the pressure gauge. Too low or too high value does not meet the specified requirements. The pressure test time and requirements should be carried out according to the standard or the order. If there is any doubt during the pressure test, the test time can be extended or re-tested. It is recommended that the valve installed in an important position should be tested twice at least. The second pressure test can only be qualified if it meets the requirements. Throttle valves are generally only tested for valve strength, packing, and flange gaskets, and dynamic sealing tests are not performed.
During the pressure test, the closing force of the valve can only be performed by a person with normal physical strength, and tools such as levers (except torque wrenches) are not allowed. However, when the diameter of the handwheel is greater than 320mm, the valve can be closed by two people. The upper sealing should be checked by valves with an upper sealing structure such as gate valves and globe valves. During the inspection, the packing gland should be loosened so that the packing is in a free state. Observe whether there is leakage in the packing. If low-pressure gas is used, then put some water over the stuffing box to see if any air bubbles leak. For valves with a driving mechanism, the test should be carried out together with the driving mechanism, and check whether the opening and closing force of the driving mechanism meets the requirements of the valve. Do not apply any grease on the sealing pair of the valve during the pressure test, except for the grease-sealed plug valve). After the valve has passed the test, the test medium in the valve cavity should be removed and cleaned, the test record should be kept. The channel should be blocked with a cover to prevent foreign matter from entering.
1. Characteristics of the valve
As a pipeline device, the valve has three characteristics: use, structure, and driving.
Characteristics of use: The use performance and scope of use are determined when a valve is designed. The use characteristics of the valve include the category of the valve, the type of the valve, the main parts of the valve, and the driving mode of the valve.
Structural characteristics: It determines some structural characteristics of valve installation, maintenance and repair. Structural characteristics are the structural length and overall height of the valve, the connection form with the pipeline, the form of the sealing seat, and the processing form of the valve stem.
Driving characteristics: There are two working characteristics of the valve; one is driven by an external force, and the other is driven by the force or medium force generated by the deformation of the internal parts of the valve.
2. Inspection of the valve
After the valve arrives at the place of delivery, the purchaser shall unpack and inspect the valve according to the requirements of the order, and carefully check whether the quantity, size, pressure rating, connection, valve body and bonnet materials, appearance quality, accessories (spare parts), and protective measures of the valve meet the requirements. After the valve is accepted, it should be placed indoors. The large-diameter valve should be placed outdoors with protective measures for inspection and testing. For the valves sent directly to the construction site, after the inspection and test, they should be placed in a clean place and covered to prevent dust and other foreign objects from entering.
3. Testing the valve
Generally speaking, the valve should be tested for valve strength and sealing performance before installation. 20% of low-pressure valves should be spot-checked, and 100% of medium and high-pressure valves should be tested to ensure the safe use of the valve.
When liquid generally water is used as the test medium, the air in the valve should be removed as much as possible to prevent the pressure value from being unstable during the pressure test. During the pressure test, the pressure should be increased gradually and slowly, and it is not allowed to increase the pressure suddenly to prevent accidents. The selection of the pressure gauge should be within 25 to 75% of the range of the pressure gauge. Too low or too high value does not meet the specified requirements. The pressure test time and requirements should be carried out according to the standard or the order. If there is any doubt during the pressure test, the test time can be extended or re-tested. It is recommended that the valve installed in an important position should be tested twice at least. The second pressure test can only be qualified if it meets the requirements. Throttle valves are generally only tested for valve strength, packing, and flange gaskets, and dynamic sealing tests are not performed.
During the pressure test, the closing force of the valve can only be performed by a person with normal physical strength, and tools such as levers (except torque wrenches) are not allowed. However, when the diameter of the handwheel is greater than 320mm, the valve can be closed by two people. The upper sealing should be checked by valves with an upper sealing structure such as gate valves and globe valves. During the inspection, the packing gland should be loosened so that the packing is in a free state. Observe whether there is leakage in the packing. If low-pressure gas is used, then put some water over the stuffing box to see if any air bubbles leak. For valves with a driving mechanism, the test should be carried out together with the driving mechanism, and check whether the opening and closing force of the driving mechanism meets the requirements of the valve. Do not apply any grease on the sealing pair of the valve during the pressure test, except for the grease-sealed plug valve). After the valve has passed the test, the test medium in the valve cavity should be removed and cleaned, the test record should be kept. The channel should be blocked with a cover to prevent foreign matter from entering.
Previous: Principles and Structural Characteristics of Elastic Seated Gate Valves
Next: Three Way Ball Valves