Reason for Defects in Welding Groove of Valves and Pipelines
Jul 29, 2023
After the low-temperature stainless steel globe valve is connected to the pipeline by butt welding, the causes of defects in the heat-affected zone and the base metal area near the valve side of the welding seam are analyzed, and the influence of the casting radiographic flaw detection standard on the defect evaluation is discussed.
1. Overview
During installation and supervisory inspection of the pipeline of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) receiving station project in a certain place, it was found that after a batch of low-temperature stainless steel globe valves imported from abroad were connected to the pipeline by butt welding, the welding seam was close to the heat-affected zone and base metal area on the valve side. After radiographic inspection, there are many bar and circular defects. The reasons for the defects were analyzed in this article.
2. Raising the question
The low-temperature stainless steel pipeline used in the LNG receiving station project is made from SS304L. The transmission medium is LNG, and the design pressure is 1.85MPa. The main valve design and manufacturing standards stipulated in the project are ASME B16.25, ASME B16.34 and BS 1873. According to data review and on-site inspection, the valves imported from abroad are low-temperature stainless steel globe valves with a size of 6 inches and 8 inches, class 150Lb, which are made from CF8; and the total quantity is 73 sets. After confirming that the valve and pipe materials are qualified products, the valve and pipe are butt-welded, and the welded joints are 100% X-ray tested (RT). According to the JB/T 4730.2 to 2005 standard, the evaluation level is II. As a result, there are many strip-shaped and round defects in the heat-affected zone and base metal area on the valve side in about 30% of the effective evaluation area of the film, while the defects on the pipe side and welding seam fusion area meet the standard range (Figure 1).
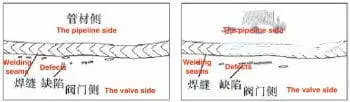
Figure 1 Inspection results of the welding seam
3. Analysis
According to the analysis of the radiographic inspection report provided by the valve supplier, the valve parts are evaluated according to ASME B16.34 (refer to ASTM E-446), and the castings (valve bodies or valve bonnets) of this batch of valves are qualified. After excluding the cause of defects caused by welding, the non-destructive testing standards adopted for valve castings are analyzed. At present, there are many kinds of RT standards for valve steel castings (Table 1). However, ASMEB16.34-2004 (refer to ASTM E-446) adopts the method of comparing pictures. There are various pictures for various defects in the standard, and users can classify defects by comparing RT films with standard films. For welding grooves, there is no grade regulation, and casting rating standards are also adopted. If the welding groove of the valve is checked and accepted according to Table 1, the grades of various defects are 2 to 4. According to the field construction experience, if the bevel of welded cast steel valves is subjected to RT inspection according to ASMEB16.34 to 2004, the control level is Grade 1 to 2 to meet the requirements of pipeline welding.
Table 1 Different defects
1. Overview
During installation and supervisory inspection of the pipeline of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) receiving station project in a certain place, it was found that after a batch of low-temperature stainless steel globe valves imported from abroad were connected to the pipeline by butt welding, the welding seam was close to the heat-affected zone and base metal area on the valve side. After radiographic inspection, there are many bar and circular defects. The reasons for the defects were analyzed in this article.
2. Raising the question
The low-temperature stainless steel pipeline used in the LNG receiving station project is made from SS304L. The transmission medium is LNG, and the design pressure is 1.85MPa. The main valve design and manufacturing standards stipulated in the project are ASME B16.25, ASME B16.34 and BS 1873. According to data review and on-site inspection, the valves imported from abroad are low-temperature stainless steel globe valves with a size of 6 inches and 8 inches, class 150Lb, which are made from CF8; and the total quantity is 73 sets. After confirming that the valve and pipe materials are qualified products, the valve and pipe are butt-welded, and the welded joints are 100% X-ray tested (RT). According to the JB/T 4730.2 to 2005 standard, the evaluation level is II. As a result, there are many strip-shaped and round defects in the heat-affected zone and base metal area on the valve side in about 30% of the effective evaluation area of the film, while the defects on the pipe side and welding seam fusion area meet the standard range (Figure 1).

Figure 1 Inspection results of the welding seam
3. Analysis
According to the analysis of the radiographic inspection report provided by the valve supplier, the valve parts are evaluated according to ASME B16.34 (refer to ASTM E-446), and the castings (valve bodies or valve bonnets) of this batch of valves are qualified. After excluding the cause of defects caused by welding, the non-destructive testing standards adopted for valve castings are analyzed. At present, there are many kinds of RT standards for valve steel castings (Table 1). However, ASMEB16.34-2004 (refer to ASTM E-446) adopts the method of comparing pictures. There are various pictures for various defects in the standard, and users can classify defects by comparing RT films with standard films. For welding grooves, there is no grade regulation, and casting rating standards are also adopted. If the welding groove of the valve is checked and accepted according to Table 1, the grades of various defects are 2 to 4. According to the field construction experience, if the bevel of welded cast steel valves is subjected to RT inspection according to ASMEB16.34 to 2004, the control level is Grade 1 to 2 to meet the requirements of pipeline welding.
Table 1 Different defects
| Defects | Types | Acceptance comparison picture E-446 |
| Gas holes | A | A2 |
| Sand inclusion | B | B3 |
| Shrinkage cavity type 1 | C | CA 2 |
| Shrinkage cavity type 2 | C | CB3 |
| Shrinkage cavity type 3 | C | |
| Shrinkage cavity type 4 | C | CD 4 |
| Hot cracks and cracks | D or E | None |
| Slag inclusions (molds or mold cores) | S | None |
The current domestic standards for valve castings are GB/T 12230-2005 and JB/T 7248-1994. The non-destructive testing standards cited are GB/T 5677 and JB/T 6440-1992. According to JB/T 6440, steel castings are not allowed to have cracks and unfused defects of internal cooling iron and mud core support. The qualified grade of RT for steel castings shall not be lower than that specified in Table 2. The standard also stipulates that for valves welded to pipelines, that is, the acceptance level of welding grooves, it should be increased by one level or implemented according to the agreement between the supplier and the buyer. When there is an agreement between the supplier and the buyer, the RT grade of the steel casting shall be implemented according to the agreement.
Table 2 Qualified grades
| Defects | Thickness, mm | |
| Less than 51 | Greater than and equal to 51 | |
| Qualification levels | ||
| Gas holes | 2 | |
| Sand or slag | 3 | 3 |
| Shrinkage cavity | 2 (threadiness) or 3 (being dendritic) | |
4. Processing
The analysis shows that there are great differences in the evaluation of welding defects due to the difference in the selection of standard systems. Therefore, if the welding groove of this batch of valves is tested by RT according to ASME B16.34 to 2004, the applicable control level should be set as level 1 to level 2. If the RT test is carried out according to the JB/T 6440 standard, the applicable grades are porosity grade 1, sand inclusion or slag inclusion grade 2, linear shrinkage cavity grade 1 and dendritic shrinkage cavity grade 2. According to the actual situation, the batch of imported valves shall be repaired or returned on site. Repair welding is performed by the supplier. After repair welding, RT inspection shall be carried out again, and those meeting the evaluation standard shall be accepted. Repair welding is only allowed once.
5. Conclusion
Since API 600, API 6D and BS 1873 and other valve design and manufacturing standards have no special regulations on the RT inspection level of valve welding grooves, when purchasing and ordering, especially from abroad, the relevant non-destructive testing, methods, parts, standards, acceptance levels and other technical conditions must be specified in the purchase contract. The size of defects within 20mm of the cast steel valve port should also be controlled. It meets the requirements of the welding seam radiographic inspection standard after welding. At the same time, it is recommended to formulate complete acceptance specifications and standards for imported valves.
Previous: Structural Principle and Performance of Double Plate Butterfly Check Valves
Next: Design of Plug Valves in the Refinery Alkylation Unit