Development and Applications of Valves for the Coal Chemical Industry
Aug 30, 2023
With the continuous improvement of coal carbonization, gasification, synthesis, processing and other links and the continuous innovation of technology, the overall competitiveness of the coal chemical industry will continue to improve. As China continues to increase the localization of coal chemical technology and equipment, the demand for high-end pipe fittings in this field will show steady growth in the future.
Technical requirements of the valve used for the coal chemical industry
1. Requirements for materials
There is oil-coal slurry in the direct coal liquefaction reaction, so the wear of coal slurry on valves, pipelines and other equipment materials is relatively common. It is required that the materials used to manufacture valves must have comprehensive properties that meet the requirements of use. It must meet the requirements of chemical composition, room temperature and high-temperature mechanical properties required by the design specifications, and have environmental embrittlement resistance that can be used for a long time in harsh environments.
2. Requirements for the process
Direct coal liquefaction not only has the characteristics of high temperature, high pressure, and hydrogenation of hydrogenation equipment, but also has the characteristics of coexistence of corrosion and wear conditions in the coal chemical industry. Therefore, the source of raw materials is very critical. Generally speaking, requirements for the corresponding clear index are put forward for the composition of valve materials, especially the content of harmful elements. The foundry should strictly control the source of raw materials. The processed raw materials should not only be smelted, but also should be further refined, especially to strengthen the control before the furnace. Only in this way can it be possible to ensure the quality of castings.
3. Requirements for structure
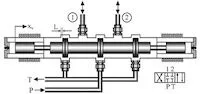
If the oil-coal slurry is not flowing smoothly or remains still, it will deposit and possibly polymerize, resulting in coking and blocking of the valve. The design of the valve structure should prevent the coking of coal slurry from making the valve fail and facilitate cleaning. At present, the cut-off valves used on the direct liquefied coal slurry pipeline are all ball valves. When the pipeline needs to be cut off and the ball valve closed, the oil and coal slurry inside the valve ball cannot be discharged and deposited in the ball cavity, which may coke and block. In fact, it is not the most suitable choice to choose a ball valve under this working condition, and its structural requirements still need to be considered.
4. High-temperature resistance
It is required that coal chemical valves are prone to difficulty in opening and closing under high-temperature conditions. The reason is that the thermal expansion between the valve core and the valve body is not synchronized. Therefore, the manufacturer should do a high-temperature opening and closing test before leaving the factory. It should be noted that in the actual use process, the valve heats up due to the high temperature of the medium. At this time, the valve core heats up first and the outer surface of the valve body heats up slowly. If the entire valve is put into the heat source, the valve body heats up first and the valve spool second, which is just the opposite of the actual working conditions, and it cannot achieve the purpose of testing. Therefore, the high-temperature opening and closing test should establish a temperature gradient consistent with the actual working conditions.
The problem with the coal chemical valve being made in China
1. Overcoming key technologies
The coal chemical valves made in China also face the problem of overcoming key technical problems. For example, the domestic matching problem of fast opening and closing high torque actuator of slag lock valves, the problem of anti-scarring and anti-scaling of valves needs to be overcome, the material of oxygen or hydrogen valves being difficult to meet the requirements of high-pressure hydrogen sulfide corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement, the improvement of the spray hardening process of corrosion resistant and erosion resistant sealing surfaces, the control of carbon, sulfur, phosphorus content of domestic materials and requirements for heat treatment.
2. Unstable operation
The stable and safe operation of production is crucial due to the particularity of the coal chemical process, and the control valve is an important part. However, the current operating status of key valves in the coal chemical industry cannot fully meet this demand. Taking the current coal chemical plant as an example, it may need to be shut down for maintenance after every 3 to 6 months of operation. The key control valve is severely scoured and corroded, and cannot operate stably for a long time, which is the bottleneck equipment that restricts the normal operation of the plant.
The future development of valves in the coal chemical industry
According to the 14th Five-Year Plan of the petroleum and chemical industry, the future development of China's coal chemical industry will gradually shift from the pursuit of quantity to quality, and from brutal expansion of production capacity to green and energy-saving development. For the dual consideration of double carbon and energy security, it is necessary to strengthen the research and development of modern coal chemical innovation technology and seek technological breakthroughs. As a breakthrough to realize double carbon, the valve needs to carry out the following self-reform:
Improve energy utilization efficiency, technical measures for energy saving and efficiency enhancement, system optimization and comprehensive utilization of existing coal chemical plants, using modern coal chemical industry to drive the upgrading of traditional coal chemical industry, eliminating outdated production capacity, and extending coal product chain. Increase the production of special fuels, high value-added products and new materials, and gradually develop in the direction of large-scale, intensification, product diversification and high-value; further reduce energy consumption, coal consumption and water consumption, and improve overall energy utilization efficiency and carbon utilization. Valve companies should also actively eliminate high-energy-consuming equipment, complete the replacement of old equipment, and adjust the energy structure, introduce automation equipment, build intelligent and electrified systems, and help the coal chemical industry to change.
The application of coal chemical valves and the coupled hydrogen energy of green electricity and green hydrogen technology does not produce carbon emissions in the process of releasing energy, and plays an increasingly important role in energy transformation. In recent years, China's green power represented by photovoltaics and wind power and the technology of electrolyzing water to produce green hydrogen have developed rapidly, and the cost of green power and green hydrogen has dropped significantly. The use of green power instead of coal power in the coal chemical process can indirectly reduce CO2 emissions in the coal chemical production process by about 5%. Sufficient sustainable green hydrogen can be produced by using electrolysis hydrogen production equipment, but the hydrogen production technology is extremely challenging; it is very important to choose stable and reliable valves to deal with the key interfaces in the hydrogen production equipment. In the future, we should innovate and develop stable and reliable valves for green hydrogen, and couple them with coal chemical green electricity and green hydrogen technology to promote the green and low-carbon transformation of the coal chemical industry.
The technology of capturing and concentrating CO2 emitted from the coal chemical industry, coal-fired power plants and petrochemical plants and then injecting it into underground storage is called CCS technology. The technology of re-storage of oil is called CCUS technology. In the coal chemical process, the decarbonization section will emit a large amount of CO2 with a purity of more than 90%. Coupling and docking with CCS/CCUS technology can reduce CO2 emissions by at least 60%. In this regard, valve companies should actively participate in CCS/CCUS demonstration projects, support the implementation of projects in terms of technology and product research and development, focus on the coal power industry where China's carbon capture technology is mainly used, and the oil industry where geological storage oil industry layout CCUS project valves are concentrated.
Technical requirements of the valve used for the coal chemical industry
1. Requirements for materials
There is oil-coal slurry in the direct coal liquefaction reaction, so the wear of coal slurry on valves, pipelines and other equipment materials is relatively common. It is required that the materials used to manufacture valves must have comprehensive properties that meet the requirements of use. It must meet the requirements of chemical composition, room temperature and high-temperature mechanical properties required by the design specifications, and have environmental embrittlement resistance that can be used for a long time in harsh environments.
2. Requirements for the process
Direct coal liquefaction not only has the characteristics of high temperature, high pressure, and hydrogenation of hydrogenation equipment, but also has the characteristics of coexistence of corrosion and wear conditions in the coal chemical industry. Therefore, the source of raw materials is very critical. Generally speaking, requirements for the corresponding clear index are put forward for the composition of valve materials, especially the content of harmful elements. The foundry should strictly control the source of raw materials. The processed raw materials should not only be smelted, but also should be further refined, especially to strengthen the control before the furnace. Only in this way can it be possible to ensure the quality of castings.
3. Requirements for structure
If the oil-coal slurry is not flowing smoothly or remains still, it will deposit and possibly polymerize, resulting in coking and blocking of the valve. The design of the valve structure should prevent the coking of coal slurry from making the valve fail and facilitate cleaning. At present, the cut-off valves used on the direct liquefied coal slurry pipeline are all ball valves. When the pipeline needs to be cut off and the ball valve closed, the oil and coal slurry inside the valve ball cannot be discharged and deposited in the ball cavity, which may coke and block. In fact, it is not the most suitable choice to choose a ball valve under this working condition, and its structural requirements still need to be considered.
4. High-temperature resistance
It is required that coal chemical valves are prone to difficulty in opening and closing under high-temperature conditions. The reason is that the thermal expansion between the valve core and the valve body is not synchronized. Therefore, the manufacturer should do a high-temperature opening and closing test before leaving the factory. It should be noted that in the actual use process, the valve heats up due to the high temperature of the medium. At this time, the valve core heats up first and the outer surface of the valve body heats up slowly. If the entire valve is put into the heat source, the valve body heats up first and the valve spool second, which is just the opposite of the actual working conditions, and it cannot achieve the purpose of testing. Therefore, the high-temperature opening and closing test should establish a temperature gradient consistent with the actual working conditions.
The problem with the coal chemical valve being made in China
1. Overcoming key technologies
The coal chemical valves made in China also face the problem of overcoming key technical problems. For example, the domestic matching problem of fast opening and closing high torque actuator of slag lock valves, the problem of anti-scarring and anti-scaling of valves needs to be overcome, the material of oxygen or hydrogen valves being difficult to meet the requirements of high-pressure hydrogen sulfide corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement, the improvement of the spray hardening process of corrosion resistant and erosion resistant sealing surfaces, the control of carbon, sulfur, phosphorus content of domestic materials and requirements for heat treatment.
2. Unstable operation
The stable and safe operation of production is crucial due to the particularity of the coal chemical process, and the control valve is an important part. However, the current operating status of key valves in the coal chemical industry cannot fully meet this demand. Taking the current coal chemical plant as an example, it may need to be shut down for maintenance after every 3 to 6 months of operation. The key control valve is severely scoured and corroded, and cannot operate stably for a long time, which is the bottleneck equipment that restricts the normal operation of the plant.
The future development of valves in the coal chemical industry
According to the 14th Five-Year Plan of the petroleum and chemical industry, the future development of China's coal chemical industry will gradually shift from the pursuit of quantity to quality, and from brutal expansion of production capacity to green and energy-saving development. For the dual consideration of double carbon and energy security, it is necessary to strengthen the research and development of modern coal chemical innovation technology and seek technological breakthroughs. As a breakthrough to realize double carbon, the valve needs to carry out the following self-reform:
Improve energy utilization efficiency, technical measures for energy saving and efficiency enhancement, system optimization and comprehensive utilization of existing coal chemical plants, using modern coal chemical industry to drive the upgrading of traditional coal chemical industry, eliminating outdated production capacity, and extending coal product chain. Increase the production of special fuels, high value-added products and new materials, and gradually develop in the direction of large-scale, intensification, product diversification and high-value; further reduce energy consumption, coal consumption and water consumption, and improve overall energy utilization efficiency and carbon utilization. Valve companies should also actively eliminate high-energy-consuming equipment, complete the replacement of old equipment, and adjust the energy structure, introduce automation equipment, build intelligent and electrified systems, and help the coal chemical industry to change.
The application of coal chemical valves and the coupled hydrogen energy of green electricity and green hydrogen technology does not produce carbon emissions in the process of releasing energy, and plays an increasingly important role in energy transformation. In recent years, China's green power represented by photovoltaics and wind power and the technology of electrolyzing water to produce green hydrogen have developed rapidly, and the cost of green power and green hydrogen has dropped significantly. The use of green power instead of coal power in the coal chemical process can indirectly reduce CO2 emissions in the coal chemical production process by about 5%. Sufficient sustainable green hydrogen can be produced by using electrolysis hydrogen production equipment, but the hydrogen production technology is extremely challenging; it is very important to choose stable and reliable valves to deal with the key interfaces in the hydrogen production equipment. In the future, we should innovate and develop stable and reliable valves for green hydrogen, and couple them with coal chemical green electricity and green hydrogen technology to promote the green and low-carbon transformation of the coal chemical industry.
The technology of capturing and concentrating CO2 emitted from the coal chemical industry, coal-fired power plants and petrochemical plants and then injecting it into underground storage is called CCS technology. The technology of re-storage of oil is called CCUS technology. In the coal chemical process, the decarbonization section will emit a large amount of CO2 with a purity of more than 90%. Coupling and docking with CCS/CCUS technology can reduce CO2 emissions by at least 60%. In this regard, valve companies should actively participate in CCS/CCUS demonstration projects, support the implementation of projects in terms of technology and product research and development, focus on the coal power industry where China's carbon capture technology is mainly used, and the oil industry where geological storage oil industry layout CCUS project valves are concentrated.
Previous: Valves Used for the Coal Chemical Industry
Next: Material Selection and Treatment of Hydrogen Peroxide Pipeline Ball Valves