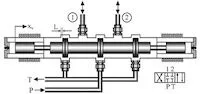
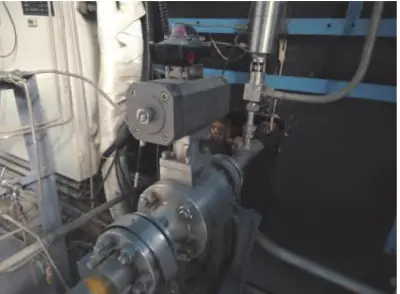
Dealing with Medium-Pressure Control Valve Failure
Oct 06, 2024
On this page
Abstract: In the operation of power plant turbines, the medium-pressure control valves play a vital role. They are responsible for regulating the amount of steam passing through the turbine, thereby controlling the power and operating efficiency of the turbine. In the power industry, ensuring the normal operation of medium-pressure control valves is essential for the stable and efficient operation of power plants. This paper proposes targeted medium-pressure control valve fault handling technologies, such as mechanical maintenance, control system adjustments, and preventive maintenance measures, with the aim of providing technical guidance to power plants for ensuring the stable operation of control valves.
Mechanical maintenance technology involves a series of complex operations and processes to ensure that the control valve maintains its optimal performance in long-term operation. The core of mechanical maintenance technology lies in the accurate diagnosis of control valve failures. This requires maintenance personnel to have a comprehensive understanding of the structure and working principles of the control valve, including the fluid dynamics, material properties, and wear and corrosion patterns inside the valve. Using professional diagnostic tools such as ultrasonic detectors, infrared thermal imagers, and vibration analyzers, maintenance personnel can accurately identify faulty components and assess their damage. After the cause of the failure is determined, mechanical repair technology involves the precise replacement or repair of damaged parts, including the replacement of severely worn valve seats and valve cores, reprocessing sealing ring surfaces, or repairing valve drive mechanisms. When performing these repair operations, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the manufacturer's specifications and standards while using appropriate tools and techniques, such as precision machining and welding techniques. After the repair is completed, the control valve must undergo full functional testing, including pressure testing, leakage testing, and flow testing, to verify that its performance has been restored to the manufacturer's specified standards.
Control system adjustment requires not only a deep understanding of electrical design but also involves complex system analysis and sophisticated adjustment techniques, requiring comprehensive consideration of control strategies, hardware performance, and overall system stability. The optimization of control strategies is the core of control system adjustment. Traditional proportional-integral-differential (PID) control is often the basis of medium-pressure control valve systems. However, as operating conditions change and the system ages, the original PID parameters may no longer be suitable forthe current system dynamics. Therefore, it is critical to readjust the PID parameters to suit current working conditions. This requires accurate measurement of the system's response characteristics, such as the valve's opening and closing speed, the rate of change of the steam flow, and the system's steady-state error, to fine-tune the PID parameters.
Preventive maintenance measures include regular inspections, performance monitoring, component replacement plans, environmental control, and technology updates. (1) Regular inspections involve visual inspections and functional tests of all key components of the medium-pressure control valve, such as checking the valve's tightness, the wear on the valve stem and seat, and the operation of the actuator. Regular inspections allow early detection and repair of minor damage or wear, preventing them from developing into more serious problems. (2) Performance monitoring is an important part of preventive maintenance. Various sensors and monitoring devices, such as pressure sensors, temperature sensors, and flow meters, monitor the operating status of the medium-pressure control valve in real time. Advanced data analysis technologies, such as trend analysis and predictive modeling, are employed to further enhance fault prediction accuracy. (3) Component replacement plans are also an important part of preventive maintenance. For components prone to wear or with limited lifespans, such as seals, filters, and lubricants, fixed replacement cycles should be established. These replacement plans should be based on the manufacturer's recommendations and actual operating wear conditions. Regularly replacing these key components effectively reduces the risk of sudden failures.
The role of medium-pressure control valves in power plant steam turbines is essential and cannot be overlooked. Performance optimization and effective fault handling of medium-pressure control valves are critical to ensuring the stable and efficient operation of power plants. In-depth research on the failure mechanisms and handling technologies of medium-pressure control valves, combining traditional maintenance methods with modern intelligent technology, can greatly enhance maintenance efficiency, improve fault prevention capabilities, and boost operational efficiency and safety.
Previous: Causes of Medium-Pressure Control Valve Failure in Power Plant Turbines
Next: Problems and Solutions in Nuclear Power Valves