Applications of Valve Management Systems in Water Supply Pipes
Jan 29, 2024
Valves play a vital role in the maintenance of the pipeline. To manage the water supply pipes well, you must manage the valves well. It is unrealistic to rely solely on manpower to manage many valves. Relying on the valve management system and applications of information management valves is an inevitable trend.
The management of water supply pipes is crucial for ensuring the efficient and effective distribution of clean water to communities. One important aspect of this management is the application of valve management systems. These systems play a vital role in controlling the flow and pressure of water within the pipes, thereby preventing leakage, reducing wastage, and improving overall system performance. Valve management systems are designed to monitor and control the opening and closing of valves in water supply networks. By accurately regulating the flow of water at different points in the pipe, these systems enable operators to respond quickly to changes in demand or emergencies such as pipe bursts or leaks. This not only helps prevent water loss but also minimizes disruption to consumers. Furthermore, valve management systems provide valuable data on system performance, allowing operators to identify areas that require maintenance or repair. By monitoring pressure levels and flow rates, these systems can detect anomalies that may indicate leaks or other issues. This proactive approach enables timely intervention before major problems occur. In addition to their practical benefits, valve management systems also contribute to sustainability efforts by conserving water resources. By minimizing leakage and optimizing system efficiency, these systems reduce unnecessary consumption and promote responsible use of this precious resource.
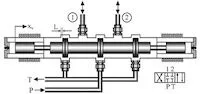
A valve is an important part of the water supply pipe. The maintenance, repair and flushing of the water supply pipe are inseparable from the operation of the valve. The quality of the valve is one of the key factors that determines whether the water supply pipe can operate normally.
1. An introduction to management systems of valves
The valve management system has a total of 7 functional modules, namely valve management, patrol management, work order management, chart statistics, problem reporting, personnel management, and system management. The type, diameter, status of opening and closing, on-site pictures and other information of any valve at any location can be checked. Inspection management can formulate inspection routes and inspection plans. Order dispatching, work order query and process can be managed through work order management. Valve statistics, inspection statistics, work order statistics and reporting statistics can be carried out through chart statistics and reports can be exported. On-site problems can be reported through problem reporting promptly. Personnel management can conduct real-time monitoring of valve operators and track historical tracks; system management can perform permissions and log management. In addition, commonly used functions such as analysis of water outages, equipment management and query, and personnel positioning can be realized.
2. Applications of management systems of valves
2.1 Inspection management of valves
Inspection and management of valves is very important, mainly for the following three reasons:
① Urban road construction has caused many valves to be buried.
② Valves are prone to water accumulation or being buried in outdoor environments.
③ The operating status of valves, including opening, closing and leaks needs to be inspected and discovered.
Since there are many valves, valve inspections must be arranged scientifically and rationally. At present, inspection routes and inspection plans for valve inspection management can be formulated. The inspection results can be fed back to the system on time. From the system, the status and on-site photos of a certain valve can be viewed, providing a basis for the maintenance and closing of valves. It is very easy to use the valve’s management system to add inspection routes and plans. Click "Map Interaction" to mark the route on the map. There are two types of routes: the first is inspection along the line, that is, marking an inspection route on the map; the second is regional inspection, which marks a patrol range on the map. Through map marking, all routes and valves within range can be selected and check-in points automatically generated. After the system distributes the valves that need to be inspected to the valve operators, the operators can log in to the valve management system on their mobile phones and navigate to the valve according to the check-in point for inspection. After the inspection, they sign in. This operation can effectively avoid missing inspections. Using the valve management system to select valves for inspection is very convenient and fast, and is more efficient than searching one by one on GIS.
2.2 Management of work orders of valves
All valve inspections, maintenance, and operations should be reported to work orders for management, and it also facilitates historical data queries. Closed-loop management is formed through system dispatch, on-site operator response of valves, and auditor review. For all work orders in the system, you can view task progress, task details, process traceability, materials, attachments, and forms. Because valves are often shut down in a planned manner, and the status of the valves that need to be closed is unknown, temporary work orders can be temporarily issued through the system and inspection personnel can be arranged to conduct preliminary inspections of relevant valves in advance.
2.3 The analysis of water outage
An important function of the valve management system is to automatically perform analysis of closed valves for pipelines that require to be closed. The minimum valve closing area is formed according to the topological relationship of the pipeline. Select the pipeline that needs emergency repair and click to start the analysis. The system can automatically analyze the minimum number of valves that need to be closed and display the positioning information of these valves to facilitate the staff to quickly find the valve. After the valve is found and the valve that needs to be closed is found, the system can mark the smallest pipeline area that may be affected to determine the minimum water outage range. If other valves need to be added after manual judgment based on the system research and judgment results, they can be added manually. After determining the valve closing range, an order is quickly dispatched to the valve operator through the valve management system. The entire process is completed by the system from analysis, valve selection, and order dispatch, which is fast and efficient, and can increase the speed of emergency repairs. The operation of shutting off the water supply and closing the valve can also form a historical record in the system to facilitate quick processing of similar situations in the future.
2.4 Personnel management
The operation of all valves on-site involves people, and personnel management is also very important. The valve management system can display the real-time location and historical trajectory of relevant operators, making it easy to understand the whereabouts of valve operators and strengthen personnel management.
The management of water supply pipes is crucial for ensuring the efficient and effective distribution of clean water to communities. One important aspect of this management is the application of valve management systems. These systems play a vital role in controlling the flow and pressure of water within the pipes, thereby preventing leakage, reducing wastage, and improving overall system performance. Valve management systems are designed to monitor and control the opening and closing of valves in water supply networks. By accurately regulating the flow of water at different points in the pipe, these systems enable operators to respond quickly to changes in demand or emergencies such as pipe bursts or leaks. This not only helps prevent water loss but also minimizes disruption to consumers. Furthermore, valve management systems provide valuable data on system performance, allowing operators to identify areas that require maintenance or repair. By monitoring pressure levels and flow rates, these systems can detect anomalies that may indicate leaks or other issues. This proactive approach enables timely intervention before major problems occur. In addition to their practical benefits, valve management systems also contribute to sustainability efforts by conserving water resources. By minimizing leakage and optimizing system efficiency, these systems reduce unnecessary consumption and promote responsible use of this precious resource.
A valve is an important part of the water supply pipe. The maintenance, repair and flushing of the water supply pipe are inseparable from the operation of the valve. The quality of the valve is one of the key factors that determines whether the water supply pipe can operate normally.
1. An introduction to management systems of valves
The valve management system has a total of 7 functional modules, namely valve management, patrol management, work order management, chart statistics, problem reporting, personnel management, and system management. The type, diameter, status of opening and closing, on-site pictures and other information of any valve at any location can be checked. Inspection management can formulate inspection routes and inspection plans. Order dispatching, work order query and process can be managed through work order management. Valve statistics, inspection statistics, work order statistics and reporting statistics can be carried out through chart statistics and reports can be exported. On-site problems can be reported through problem reporting promptly. Personnel management can conduct real-time monitoring of valve operators and track historical tracks; system management can perform permissions and log management. In addition, commonly used functions such as analysis of water outages, equipment management and query, and personnel positioning can be realized.
2. Applications of management systems of valves
2.1 Inspection management of valves
Inspection and management of valves is very important, mainly for the following three reasons:
① Urban road construction has caused many valves to be buried.
② Valves are prone to water accumulation or being buried in outdoor environments.
③ The operating status of valves, including opening, closing and leaks needs to be inspected and discovered.
Since there are many valves, valve inspections must be arranged scientifically and rationally. At present, inspection routes and inspection plans for valve inspection management can be formulated. The inspection results can be fed back to the system on time. From the system, the status and on-site photos of a certain valve can be viewed, providing a basis for the maintenance and closing of valves. It is very easy to use the valve’s management system to add inspection routes and plans. Click "Map Interaction" to mark the route on the map. There are two types of routes: the first is inspection along the line, that is, marking an inspection route on the map; the second is regional inspection, which marks a patrol range on the map. Through map marking, all routes and valves within range can be selected and check-in points automatically generated. After the system distributes the valves that need to be inspected to the valve operators, the operators can log in to the valve management system on their mobile phones and navigate to the valve according to the check-in point for inspection. After the inspection, they sign in. This operation can effectively avoid missing inspections. Using the valve management system to select valves for inspection is very convenient and fast, and is more efficient than searching one by one on GIS.
2.2 Management of work orders of valves
All valve inspections, maintenance, and operations should be reported to work orders for management, and it also facilitates historical data queries. Closed-loop management is formed through system dispatch, on-site operator response of valves, and auditor review. For all work orders in the system, you can view task progress, task details, process traceability, materials, attachments, and forms. Because valves are often shut down in a planned manner, and the status of the valves that need to be closed is unknown, temporary work orders can be temporarily issued through the system and inspection personnel can be arranged to conduct preliminary inspections of relevant valves in advance.
2.3 The analysis of water outage
An important function of the valve management system is to automatically perform analysis of closed valves for pipelines that require to be closed. The minimum valve closing area is formed according to the topological relationship of the pipeline. Select the pipeline that needs emergency repair and click to start the analysis. The system can automatically analyze the minimum number of valves that need to be closed and display the positioning information of these valves to facilitate the staff to quickly find the valve. After the valve is found and the valve that needs to be closed is found, the system can mark the smallest pipeline area that may be affected to determine the minimum water outage range. If other valves need to be added after manual judgment based on the system research and judgment results, they can be added manually. After determining the valve closing range, an order is quickly dispatched to the valve operator through the valve management system. The entire process is completed by the system from analysis, valve selection, and order dispatch, which is fast and efficient, and can increase the speed of emergency repairs. The operation of shutting off the water supply and closing the valve can also form a historical record in the system to facilitate quick processing of similar situations in the future.
2.4 Personnel management
The operation of all valves on-site involves people, and personnel management is also very important. The valve management system can display the real-time location and historical trajectory of relevant operators, making it easy to understand the whereabouts of valve operators and strengthen personnel management.
Previous: Ceramic Valves Used in Production
Next: Internal Leakages of Ball Valves