Ball Valves
What is a ball valve?

API 6D Floating Ball Valves, A216 WCB, 4 Inches, 150 LB, RF
Carbon Steel Floating Ball Valve, API 6D, WCB, 3 Inch, CL150
API 6D Floating Ball Valve, ASTM A216 WCB, 2 Inches, 300 LB
ASTM A216 WCB Floating Ball Valve, API 6D, 2 Inch, CL150, RF
Forged Floating Ball Valve, API 608, A350 LF2, DN25, PN250
Full Bore Floating Ball Valve, API 608, LF2, 1 Inch, CL150
API 608 Floating Ball Valves, A350 LF2, 4 Inch, 150 LB, RF
ASTM A350 LF2 Floating Ball Valves, API 608, DN25, PN63, RF
API 608 ASTM A105N Ball Valve, 2 IN, CL150, Soft Seated, RF
API 6D Bronze Ball Valve, ASTM B148 C95800, 2 IN, 150 LB, RF
API 608 Ball Valves, ASTM B148 C95800, 3/4 IN, 150 LB, RF
Carbon Steel A105N Ball Valve, API 608, 1/2 IN, 800 LB, BB
The advantages of ball valves
Low resistance
A ball valve has the lowest flow resistance, which is 0.Withstanding high-pressure difference
The closing part can withstand the high-pressure difference when the ball valve is closed.Complete sealing
Complete sealing can be achieved in a wide range of pressure and temperatures.Fast opening and closing
A ball valve can be opened and closed quickly, and the opening and closing time for ball valves with some structures is only 0.05 to 0.1 seconds to ensure that it can be used in the automation system of the test bench. When the ball valve is opened and closed quickly, there is no shock in operation.No corrosion for the sealing surface
When the ball valve is fully opened and fully closed, the sealing surface of the sphere and the valve seat is isolated from the medium, so the medium passing through the valve at high speed will not cause corrosion of the sealing surface.Long service life
The ball valve with a fully welded valve body can be directly buried below ground, so that the valve internals will not be corroded, and its maximum service life can reach 30 years. It is an ideal valve for oil and natural gas pipelines.No stucking
A ball valve is not stuck when working without lubricant, which can be reliably used in corrosive media and liquids with low boiling points.Light weights
A ball valve has compact structure and light weights, which can be considered the most reasonable valve structure for a low-temperature medium system.Bearing the stress
The mesh body is symmetrical, and the welded valve body structure, can well withstand the stress from the pipeline.Automatic positioning
The spherical closing part can be automatically positioned at the boundary position.Good sealing
The working medium is reliably sealed on both sides.
Applications of ball valves
Parts of ball valves
The basic parts of ball valves are as follows:Valve bodies
According to the structure of the valve body, the ball valve can be divided into vertical symmetrical split ball valves, asymmetric split ball valves, three-piece split ball valves, inclined split ball valves and one-piece ball valves. There are two positions for the parting surface; one is the eccentric split type, and the parting surface is near the downstream side; the other is the symmetrical split type, and the parting surface is on the center line of the valve shaft. The parting surface of asymmetric split valve bodies avoids the valve shaft, which can prevent the problem of leakages due to poor sealing and bonding between the seal at the valve shaft and the parting surface of the valve body. Asymmetric split ball valves are usually used for large ball valves. The oblique split valve body is usually used for small and medium ball valves. The symmetrical split valve body is usually used for small ball valves. The one-piece valve body is limited by transportation and processing conditions because the valve body is not removable and the processing is more complicated.
Spheres
The sphere is the opening and closing part of the ball valve, which is also known as the core or the ball. The ball rotates around the center line of the valve body to open and close the ball valve. The ball valve and the plug valve are the same types of valve, and the ball valve also evolved from the plug valve. However, the closing part of the ball valve is a sphere. Ball valves with different functions often have different spheres. Balls are usually divided into two categories, that is, soft-sealed balls and metal-sealed balls. The ball can be divided into two-way balls, three-way balls, four-way balls, curved balls, floating balls, trunnion balls, V-shaped balls, eccentric hemispheres, handle balls, solid balls and hollow balls according to functions.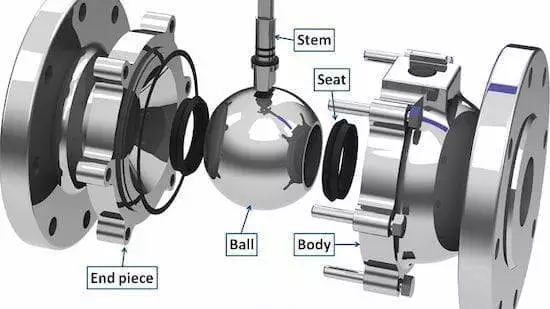
Seats
The sealing principle of the ball valve seat varies according to its structure. The commonly used valve seat structure can be divided into two categories, including trunnion seats with floating balls and floating seats with trunnion balls. When the valve seat is fixed and the ball floats, the ball will be displaced in the direction of fluid flow under the action of fluid pressure, so that it is sealed with the valve seat behind the valve and in closer contact, that is, the specific pressure on the sealing surface increases, forming a single-sided sealing. At the same time, the specific pressure on the sealing surface of the valve seat before the valve is correspondingly reduced, and the sealing is often not guaranteed. When the floating ball of the valve seat is fixed, the fluid pressure cannot cause the ball to displace, but the valve seat is pressed against the ball using a spring or fluid thrust to establish a sealing-specific pressure. According to the sealing material, the ball valve seat is divided into soft-sealed valve seats and metal-sealed valve seats.Shafts
The shaft connects the ball to the control mechanism that rotates the ball. O-rings and packing rings are used to seal the shaft and the bonnet to prevent leakages of the fluid.Bonnets
The bonnet is the valve part with the stem and packing installed to connect or support the actuator. The valve bonnet and the valve body can be integrated or separated. The valve bonnet is the top cover, which is a detachable part of the valve body assembly. It is usually connected to the valve body by high-impact bolts. It is a pressure-bearing part. Therefore, it has the same design conditions as the valve body housing. The valve bonnet needs to be removed first to remove the internal parts of the valve. There are two uses for the valve bonnet. One is to position the valve stem to ensure the normal transmission switch of the adjusting rod. The second is the sealing effect, which has a certain strength to prevent the internal fluid from leaking.Packing
A flexible seal installed around the shaft avoids the medium from flowing through the valve and escaping outside the valve.Actuator
Actuators use liquid, gas, electricity, or other energy sources and convert them into driving action through motors, cylinders, or other devices. The actuator is used to drive the valve to the fully open or fully closed position. There are gear, lever, electric, motor-operated, hydraulic and pneumatic actuators.
Ball valves classified by materials
Carbon steel ball valves
Carbon steel ball valves refer to ball valves made from carbon steel. The carbon steel ball valve is mainly used for cutting and distributing the medium and changing the flow direction of the medium in the pipeline. It can be closed well only by rotating at an angle of 90 and with small torque.
Stainless steel ball valves
Stainless steel ball valves can be used to control the flow of various types of fluids such as air, water, steam, various corrosive media, mud, oil, liquid gold and radioactive media. The commonly used stainless steels include SS316, SS304 and ASTM A351 CF8M.
Duplex steel ball valves
Duplex steel ball valves adopt the top entry structure, which reduces the connecting bolts of the valve body under the condition of high pressure and large diameters, which enhances the reliability of the valve and can overcome the influence of the system weight on the normal operation of the valve. Duplex steel ball valves are widely used in coal chemical, petrochemical, rubber, paper, pharmaceutical and other pipelines.
Super duplex steel ball valves
Super duplex steel ball valves include 2pc, 3pc, flanged and unibody super duplex steel ball valves.
Brass ball valves
Brass ball valves have features of multi functions, easy operation, and easy installation. They can be used in both residential and commercial plumbing jobs. With a simple quarter twist of the handle, the medium is cut off.
Plastic ball valves
Plastic ball valves include PVC, PP, GFPP, PVDF and PE ball valves, which are suitable for cutting off corrosive media. The working temperature is -14℃ to 100℃ and -40℃ to 140℃ according to different materials. The plastic ball valve has excellent corrosion resistance. The sealing ring adopts F4, which has excellent corrosion resistance and extended service life, flexible rotation and easy operation. The integral ball valve has few leakage points, and high strength, and the connection-type ball valve is easy to assemble and disassemble. Plastic ball valves can be classified into flanged plastic ball valves, threaded plastic ball valves and socketed plastic ball valves.
Ball valves classified by temperatures
Cryogenic ball valves
Cryogenic ball valves can be operated safely and reliably at a very low temperature. They are usually made from stainless steel, which makes them have good corrosion resistance, even when they are exposed to aggressive fluids. The working temperature of cryogenic ball valves is from -196°C to +165°C. Cryogenic ball valves are suitable for dispensing liquid gases, storing liquid gases, or connecting cryogenic pumps.
High-temperature ball valves
The high-temperature ball valve has a metal sealing structure, which adopts metal-to-metal sealing. The butterfly plate of the high-temperature ball valve is installed in the diameter direction of the pipeline. In the cylindrical passage of the hard-sealed ball valve body, the disc-shaped plate rotates around the axis, and the rotation angle is between 0° and 90°. When it rotates to 90°, the valve is fully open. The high-temperature ball valve has features of compact structure, reliable sealing, simple structure and convenient maintenance. The sealing surface and the spherical surface are often in a closed state, which is not easy to be scoured by the medium and is easy to operate and maintain. The high-temperature ball valve is suitable for general working media such as water, solvent, acid and natural gas, as well as media with harsh working conditions such as oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, methane and ethylene. The ball valve body can be integral or combined.
Insulation jacketed ball valves
The insulation ball valve is a ball valve with a welded metal jacket, which is used for steam or other heat preservation and cold preservation medium to ensure that the medium in the valve can work normally. According to the structure of the ball valve, the insulation jacketed ball valve has several structural forms, such as integral insulation ball valves, two-piece insulation ball valves, and wafer insulation ball valves. The insulation ball valve has good thermal and cold insulation, and the diameter of the valve is consistent with that of the pipe, which can effectively reduce the heat loss of the medium in the pipeline. The insulation ball valve is mainly used in petroleum, chemical, metallurgy, pharmaceutical, food and other systems to transport media with high viscosity that will solidify at room temperatures. Compared with ordinary ball valves, the insulation ball valve has smaller sizes, lighter weights, no leakage, and good sealing performance.

Ball valves classified by the design of the sphere
Floating ball valves
The sphere of the floating ball valve is supported by the valve seat. There are two sealing rings for valve seats in the valve body of the floating ball valve, and a sphere is clamped between them. There is a through hole on the sphere. With the help of the valve stem, the sphere can rotate freely in the sealing of the valve seat. When the ball valve is opened, the sphere hole is aligned with the pipe diameter to ensure the minimum resistance of working media in the pipe. When the valve stem rotates 1/4 turn, the ball hole is perpendicular to the channel of the valve, and the ball is tightly pressed on the valve seat’s sealing ring at the outlet end by the pre-tightening force and medium pressure applied to sealing rings of two valve seats to ensure that the valve is completely sealed.
Trunnion mounted ball valves
The trunnion-mounted ball valve is provided with a valve stem on the upper and lower sides of the valve sphere to fix it. The trunnion-mounted ball valve is a new generation of high-performance ball valves, which is suitable for long-distance pipelines and general industrial pipelines. Special consideration has been given to its strength, safety, and resistance to harsh environments. The trunnion-mounted ball valve is suitable for various corrosive and non-corrosive media. It has small torque, small deformation of the valve seat, stable sealing performance and long service life, and is suitable for pipelines with high pressure and large diameters.
Vented ball valves
A vented ball valve has a hole on the upstream portion of the ball, which is very small and acts as a pressure regulator, so that the pressure in the valve can be maintained the same as that of the system. The purpose of the drilled hole is to discharge the gas and avoid leakages, failures and explosions. A vented ball valve is applied to volatile liquids, compressed air systems and cryogenic processing.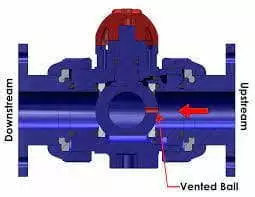
Ball valves classified by housing assembly
One-piece ball valves
A one-piece ball valve is a relatively new type of ball valve. It has the advantages of no friction for opening and closing, the sealing being not easily worn, and small opening and closing torque. It is widely used for water supply and drainage in petrochemical cities and other working conditions that require strict cut-offs.
Two-piece ball valves
A two-piece ball valve consists of two pieces. One piece consists of one end and the body, and the other piece holds the trim and the other end. Once the two-piece ball valve is installed, it can’t be repaired without uninstallation.
Three-piece ball valves
A three-piece ball valve consists of three pieces, that is, the two ends and a valve body. The two ends are usually welded or threaded to the pipeline, so that the valve body can be removed for repair, leaving the other two sections still threaded into your system.
Ball valves classified by bore profile
Full bore ball valves
A full bore ball valve is a valve whose bore diameter is similar to that of the pipe, resulting in a big size for the ball and a higher price than a reduced bore. It has a constant flow area for the fluid, so the flow resistance is very low. It is easy to maintain and clean a full bore ball valve. Full-bore ball valves can also be used to transport liquids containing mixed solids, where flow restriction can lead to particle building up that can eventually cause separation of the mixture flowing through it. The full bore ball valve is generally used in pipelines for conveying viscous and slagging media. There is no flow resistance because of its small fluid resistance, and it is convenient for regular wax scraping and purging to pass through. For pipelines that require regular pigging, full-bore ball valves must be used regardless of the medium being transported. The flow will not be reduced for the medium in the full-bore ball valve. It is an ideal product for pipeline control, especially in strict working conditions. When the main pipelines of oil pipelines and gas pipelines need to be buried underground, full-bore welded ball valves must be used.
Reduced bore ball valves
A reduced bore ball valve is a valve whose bore diameter is smaller than that of the pipe. The reduced bore ball valve is suitable for pipelines that transport gas or media with physical properties similar to water, because its weight is about 30% lighter than that of the full bore ball valve, and its flow resistance is only about 1/7 that of the globe valve with the same diameter. It is beneficial for reducing pipeline load and costs. The reduced bore ball valve is suitable for some working conditions with low requirements and low requirements for flow resistance. Compared with other valves, the reduced bore ball valve has a smaller pressure drop.
Segmented ball valves
A segmented ball valve is a kind of valve which has a V-shaped notch on its ball. It has good rangeability, control, and shut-off capability. The V-shaped notch ball can provide positive shearing action and has a feature of an inherent equal percentage flow, which achieve the purpose of no blocking and controlling flows. When a segmented ball valve’s ball reaches the fully opened position, the flow rate increases exponentially.
Ball valves classified by sealing materials
Soft-sealed ball valves
The general soft-sealed valve refers to valves whose valve cores or valve seats adopt a non-metallic material, mainly polytetrafluoroethylene and rubber. The soft seal needs to be fireproof, because leakages will occur for the material of the soft sealing at high temperatures. The soft sealing cannot be used on some occasions, for example, in some corrosive media. The soft seal valve has the best sealing effect, but debris such as welding slags and iron filings may be left in the installation and cleaning of the pipeline system. Therefore, the cleaning of the medium and the strict flushing of the pipeline must be considered when selecting the soft sealing structure before it is put into operation.
Metal-sealed ball valves
The metal seal valve is a valve whose sealing surfaces and valve seats are all metal, and its machining accuracy and process are difficult. It is generally used for high pressure, usually above 2.5MPa. The metal-sealed valve has a long production cycle and complex processing. The selection of soft and metal-sealed valves is mainly based on the medium, temperature and pressure. Generally, when the medium contains solid particles or the temperature is higher than 200 degrees, it is best to use a metal-sealed ball valve.
Ball valves classified by connection ends
Threaded ball valves
A threaded ball valve is a valve whose closing part is a sphere, and the sphere rotates around the center line of the valve body to achieve the purpose of opening and closing. Ball valves are mainly used to cut off and distribute the medium and change the flow direction of the medium in the pipeline. A threaded ball valve is a kind of ball valve, and it is connected to the pipeline by thread ends. It is mainly used for low-pressure, small-diameter pipelines with nominal pressure PN 16 to 140 and nominal size DN 8 to 50.
Welded ball valves
The welded ball valve body is integrally welded, and there will be no external leakage. The valve seat is composed of a PTFE sealing ring and a spring, which has good adaptability to changes in pressure and temperatures, and no leakage will occur within the scope of use. There is a PTFE self-sealing gasket and an O-ring at the bottom of the valve stem, and there are 2 O-rings and two PTFE sealing gaskets on the top to ensure no leakage. The material of the valve body is the same as that of the pipeline, and there will be no uneven stress, nor will it be squeezed and deformed due to earthquakes and vehicles passing through the ground. The valve body is light and easy to keep warm. The directly buried ball valve can be directly buried in the ground, and there is no need to build tall valve wells; only small shallow wells are needed on the ground, which greatly saves construction costs and engineering time. The length of the valve body and the height of the valve stem can be adjusted according to the requirements for the construction and design of the pipeline.
Flanged ball valves
A flanged ball valve is especially suitable for media containing fibers and tiny solid particles. The flanged ball valve has features of compact structure, reliable sealing, simple structure, and easy maintenance. The sealing surface and spherical surface of the flanged ball valve are often in a close state, which is not easily eroded by the medium, easy to operate and maintain, and suitable water, solvent, acid and natural gas, oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, methane and ethylene.
Wafer ball valves
The wafer ball valve has a simple structure, small sizes and light weights, and only consists of a few parts. It can be quickly opened or closed by rotating 90°. The unique eccentric design of the wafer ball valve enables frictionless transmission between the sealing surfaces, extending the service life of the valve. The elastic seal is produced by torque. The ingenious wedge-shaped design enables the valve to have the automatic sealing function of tightening, and compensation and zero leakage can be obtained for the sealing surfaces. According to the requirements of the user, pneumatic and electric devices can be provided to meet the needs of remote control and program control. The material of the parts can be replaced for various media, and the lining such as F46, GXPP and PO can be corrosion resistant.
Clamped ball valves
The clamp ball valve mainly consists of three parts, that is, sealing rubber rings, clamps and locking bolts. The rubber sealing ring on the inner layer is placed on the outside of the connected pipe, and is in line with the pre-rolled groove; a clamp is fastened on the outside of the rubber ring, and then fastened with two bolts. The groove connection has good sealing performance due to the unique sealable structure design of its rubber sealing rings and clamps, and with the increase in fluid pressure in the pipe, its sealing performance is correspondingly enhanced. Clamped ball valves have been used in chemical and petrochemical industry, low-temperature materials in refrigeration, and materials required for hygiene in the production of light industrial food and pharmaceuticals due to their compact structure, simple operation, long service life, safety and reliability.











